The Wolfram Solution forOpticsOptimize systems of symbolically defined lenses and mirrors, test optical components with built-in image processing or data analysis functions, and calculate complex ray-tracing models. The Wolfram optics solution integrates these capabilities with built-in special functions, advanced differential equation solvers, and the most automated and reliable computation, development, and deployment environment available. |
 |
Wolfram technologies include thousands of built-in functions and curated data on many topics that let you:
- Quickly simulate behavior of lenses, mirrors, and other optical components
- Design solar concentrators, lasers, camera lenses, and more
- Animate graphics to see how results change while adjusting optical components
- Create interactive interfaces for designing optical systems or performing analyses
- Design, test, and interact with light scattering instruments
- Use high-powered mathematics to optimize designs, reducing research time and expense
- Perform optical modeling for microlithography or optimize microscopy instrumentation
- Visualize interferograms to test mirrors and lenses
- Optimize pulse formation and control in new laser designs
- Develop new imaging techniques for research in a variety of scientific or medical fields
In addition, the application package Optica offers a ray-tracing engine and a searchable component database of more than 6,800 commercial optical parts, all fully integrated.
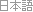
Interactive models of the human eye and other optical systems
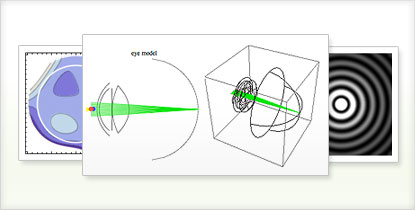
Model light refraction within a water droplet
Does your current tool set have these advantages?
-
Create interactive tools for designing optical systems, curve fitting, or data analysis that provide visual feedback to make debugging and testing innovative instrumentation easier
Code V and Zemax do not offer custom interactive tools -
Get accurate results in optical model calculations with fully automated precision control and arbitrary-precision arithmetic
Matlab and other systems relying on machine arithmetic can show critical errors due to numerical accuracy failure -
Rapidly prototype new algorithms more quickly than in other software by choosing from procedural, functional, and rule-based programming paradigms as desired
Code V and Zemax use a procedural language -
Import or acquire data, analyze it, and deliver results in one document instead of across several applications
Unique to Wolfram technologies -
Highly optimized superfunctions analyze your equations and automatically select the right algorithms to get accurate results quickly—sometimes switching mid-calculation for further optimization
Other computation systems make you analyze your equations manually to determine which function to apply—for example, where in the Wolfram Language you use NDSolve, in Matlab you must correctly choose among ode45, ode23, ode113, ode15s, bvp4c, pdepe, and so on, or risk wrong answers

Create interactive tools for visualizing optical phenomena
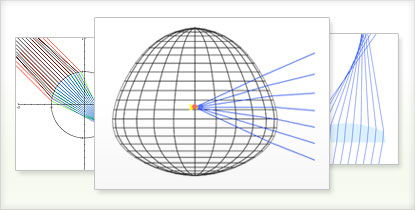
Model core density profiles of optical fibers
Optics specific capabilities:
- Both numeric and symbolic computations for accurately calculating reusable models or determining aberrations
- Perform optical calculations from point spread functions to full theories of microscopes with calculus and differential equation solving capabilities »
- Built-in optical special functions including Fresnel integrals, Zernike polynomials, and Bessel functions »
- Automated precision control with specified input or output precision to automatically adjust computations to maintain or achieve precise results
- Advanced statistical and curve fitting functions for analyzing data »
- Functions for automatically computing probabilities and expectations of any event, allowing quick calculations for many problems
- Perform convolutions and correlations on numerical data to deblur and denoise images »
- Use image processing and filtering functions to model the effects of diffraction, perform deconvolutions, and more, using built-in functions and your own custom algorithms »
- 2D and 3D graphing capabilities for standard optical plots, including scatter, density, and contour plots »
- Access curated scientific data from Wolfram|Alpha, immediately ready for analysis, interactively or programmatically »
- Powerful programming language and built-in parallel computing for developing new analysis algorithms or solving complicated ray-tracing problems
- Integration with C/C++, Python, Java, .NET, databases, and other applications »
- Sequential and nonsequential ray-tracing, symbolic optical functions, and optimization of three-dimensional optical systems, plus access to a database of optical materials and commercial parts and components with Optica