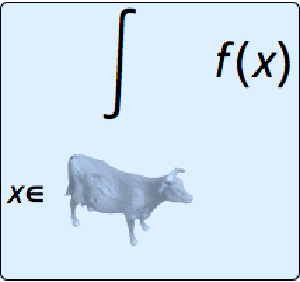Integrate over Regions
Integrate over any region. The actual integral used depends on the dimension of the region: a curve integral for one-dimensional integrals, a surface integral for two-dimensional regions, etc. Integrals can be computed symbolically or numerically.
The curve length is an integral over a curve.
| In[1]:= | X |
| Out[1]= |
| In[2]:= | X |
| Out[2]= |
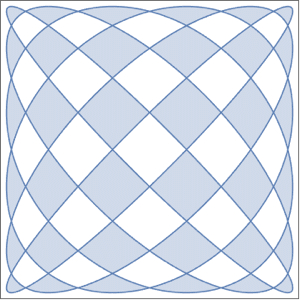
The surface area is an integral over a surface.
| In[3]:= | X |
| Out[3]= |
| In[4]:= | X |
| Out[4]= |
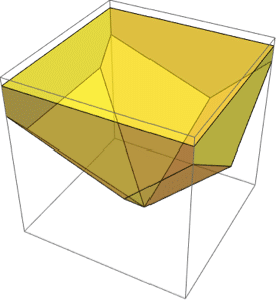
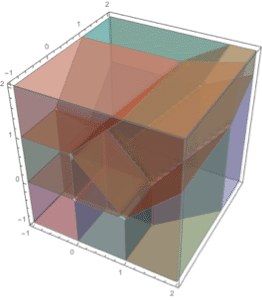
The solid volume is an integral over a solid.
| In[5]:= | X |
| Out[5]= |
| In[6]:= | X |
| Out[6]= |
Integrate in any number of dimensions.
| In[7]:= | X |
| Out[7]= |
Use symbolic vector variables.
| In[8]:= | X |
| Out[8]= |
| In[9]:= | X |
| Out[9]= |
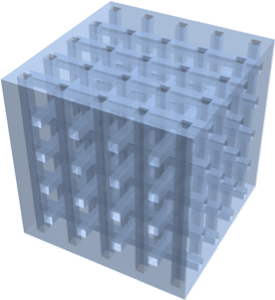
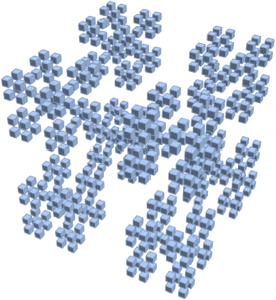
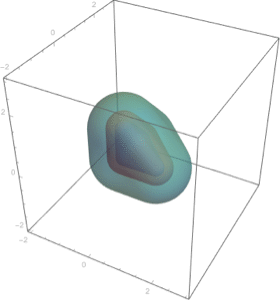
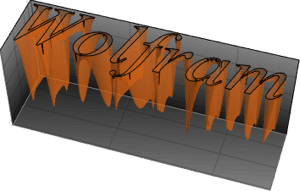
Integrate over any region.
| In[10]:= | 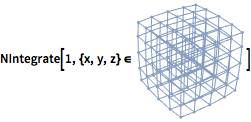 X |
| Out[10]= |
| In[11]:= | 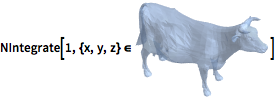 X |
| Out[11]= |
| In[12]:= | 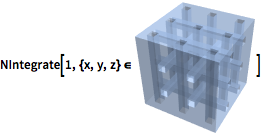 X |
| Out[12]= |