Wolfram控制系统Wolfram 语言
的核心内容
建模、设计、部署。
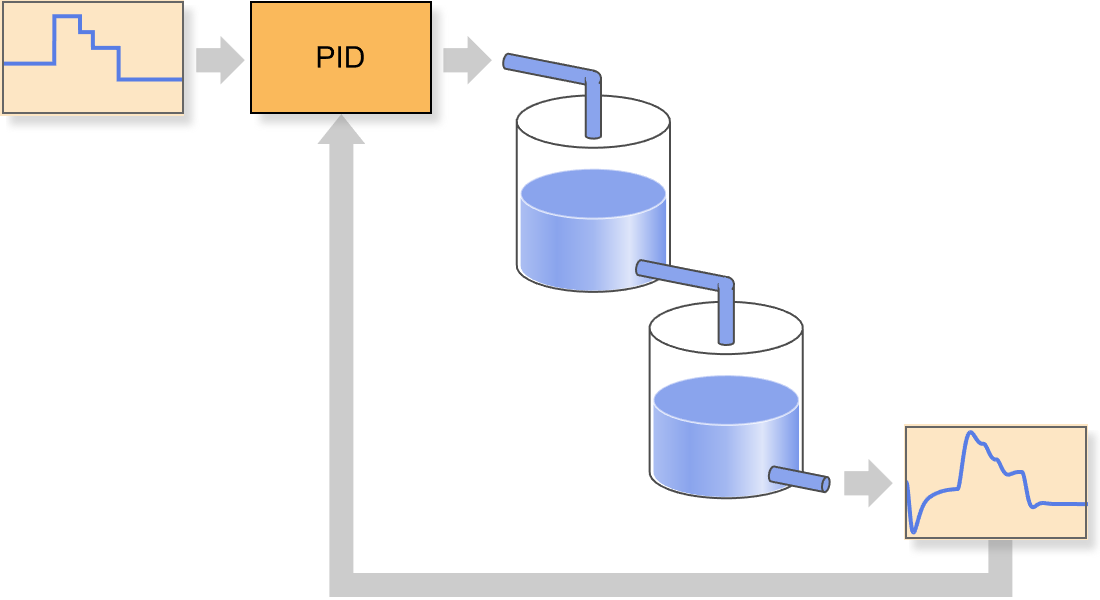
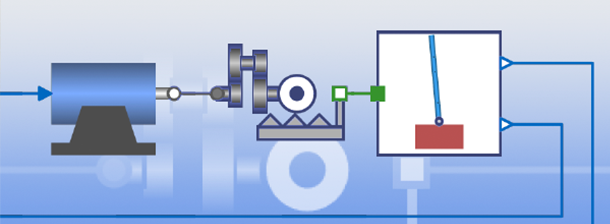
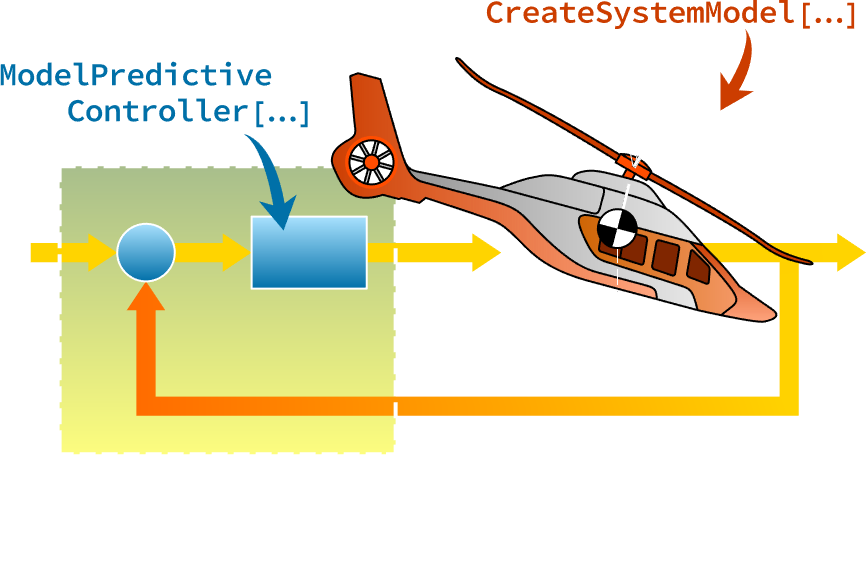
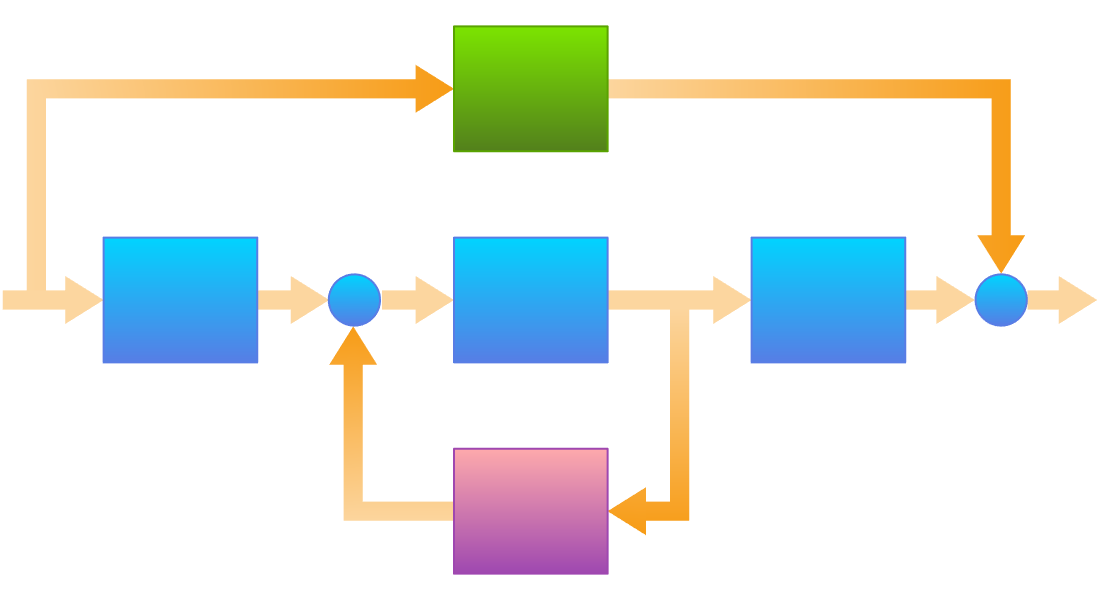
对环境进行建模。设计一个控制器。部署到现实世界。可在高度集成的工作流程中完成所有上述任务,为学习者和专业人士开发。
基于模块的模型
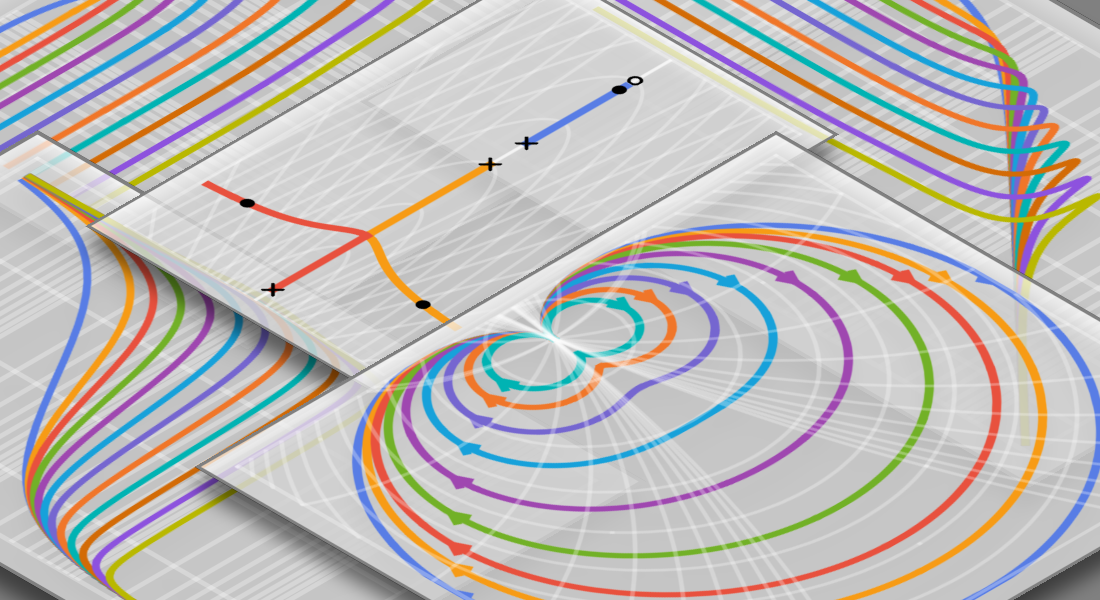
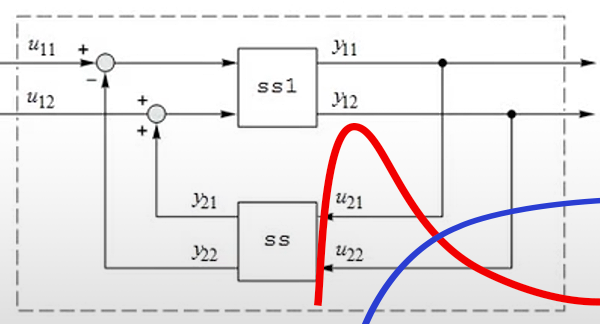
直接创建,也可从微分或差分方程创建状态空间或传递函数模块。将它们连接起来形成更大的系统。用生成的模型进行分析、设计和部署。
基于组件的模型
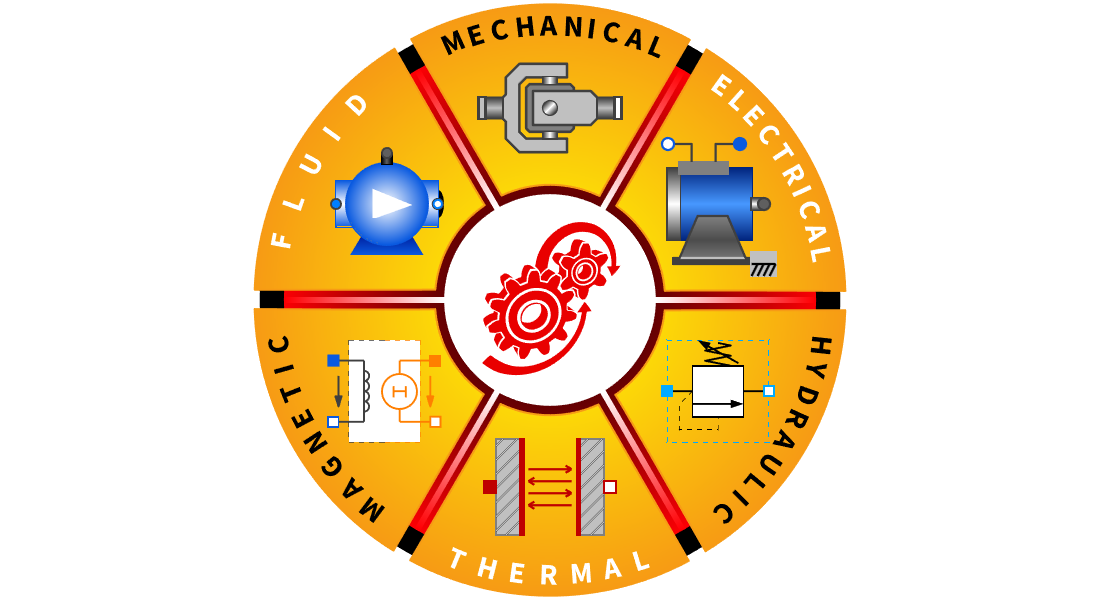
像乐高积木一样拖放和连接模型组件,获取高质量多域模型。用它们进行仿真、验证,并导出用于控制设计的基于模块的模型。
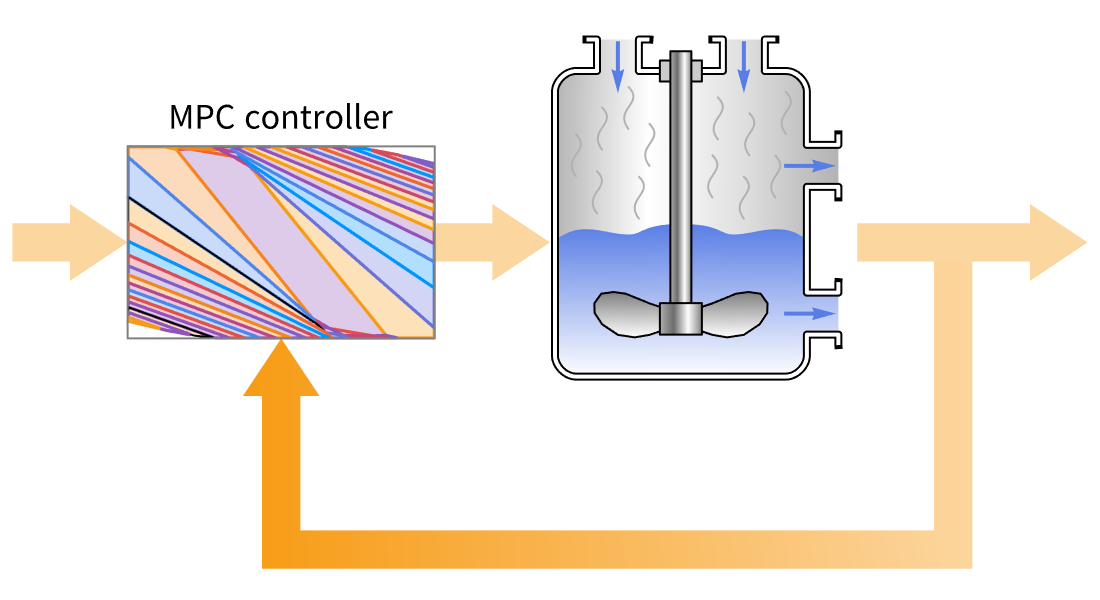
MPC 设计
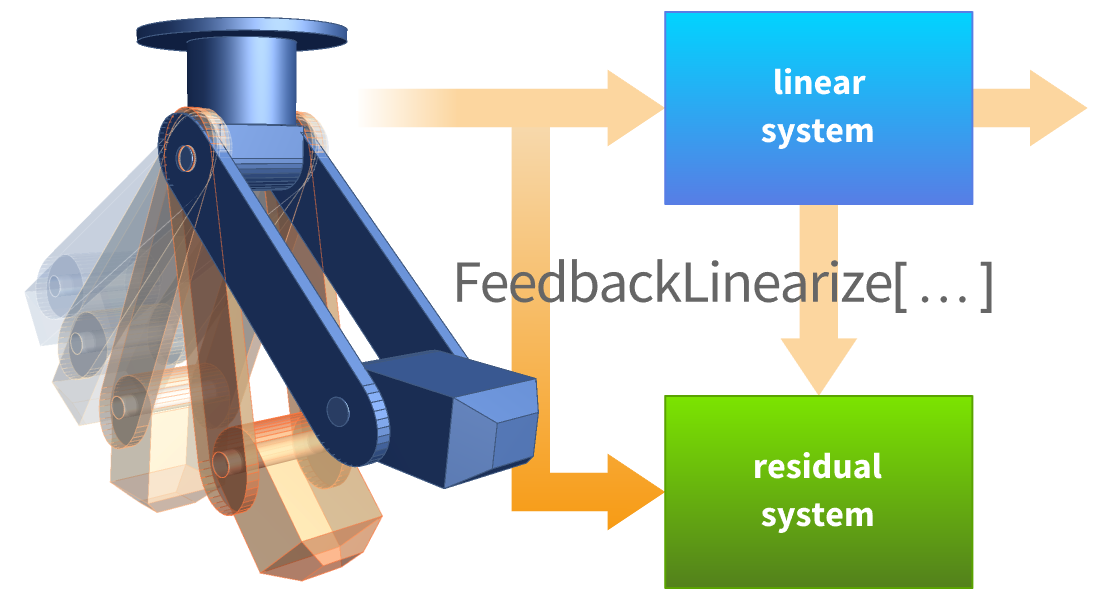
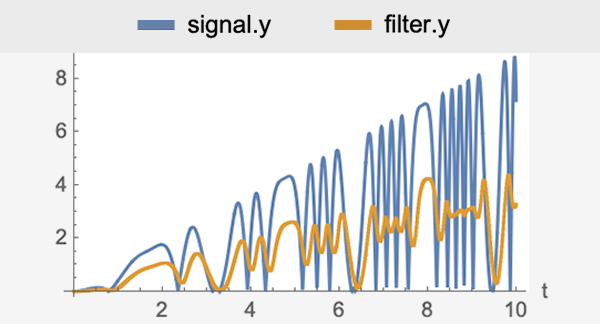
通过自动使用离线参数优化,为快速采样应用和计算能力有限的应用设计显式模型预测控制器 (MPC)。解决 1-、平方 2- 或 ∞-范数成本函数最小化的约束调节或跟踪问题。
FMI 部署
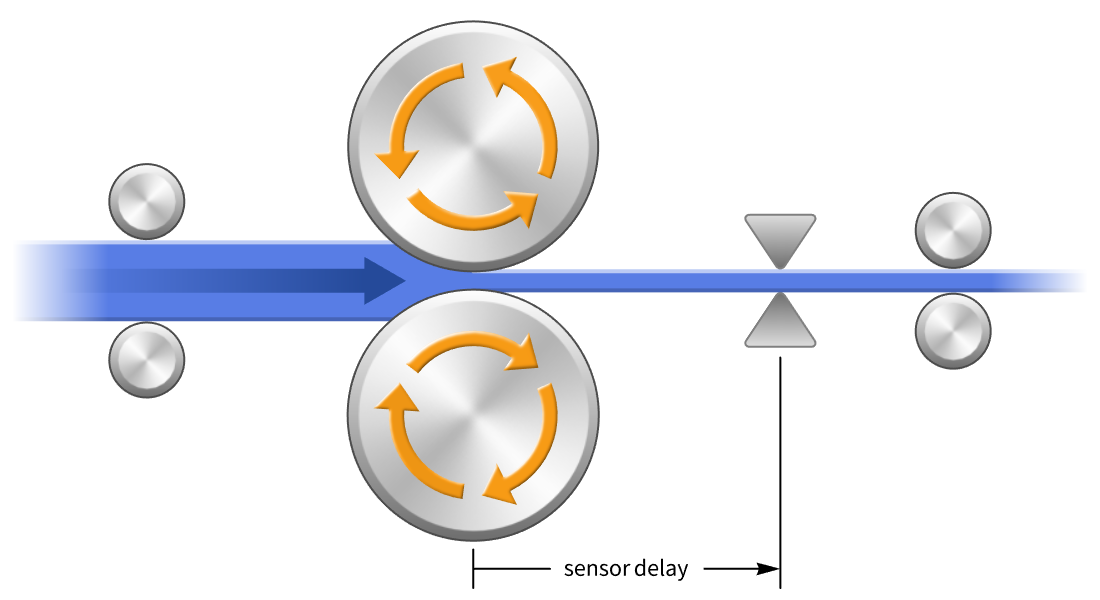
将控制器作为功能模型单元 (FMU) 部署到其他 100 多个与 FMI 兼容的工具。在子系统由不同公司和工具设计的环境中进行有效协作。及早发现缺陷并避免严重的下游集成问题。

Wolfram 控制系统的相关参考资料
Wolfram 控制系统是 Wolfram 语言的一个组成部分。整个系统包含了六千多个内置函数,涵盖了计算领域的方方面面,所有内容被精心集成在一起,相互支持,完美地结合为一个整体。
所有资料与参考文档
AffineStateSpaceModel ▪ AsymptoticOutputTracker ▪ BodePlot ▪ CarlemanLinearize ▪ ContinuousTimeModelQ ▪ ControllabilityGramian ▪ ControllabilityMatrix ▪ ControllableDecomposition ▪ ControllableModelQ ▪ DescriptorStateSpace ▪ DiscreteInputOutputModel ▪ DiscreteLQEstimatorGains ▪ DiscreteLQRegulatorGains ▪ DiscreteTimeModelQ ▪ DualSystemsModel ▪ EstimatorGains ▪ EstimatorRegulator ▪ FeedbackLinearize ▪ FeedbackSector ▪ FeedbackSectorStyle ▪ FeedbackType ▪ FullInformationOutputRegulator ▪ GainMargins ▪ GainPhaseMargins ▪ InternallyBalancedDecomposition ▪ JordanModelDecomposition ▪ KalmanEstimator ▪ KroneckerModelDecomposition ▪ LinearizingTransformationData ▪ LQEstimatorGains ▪ LQGRegulator ▪ LQOutputRegulatorGains ▪ LQRegulatorGains ▪ MinimalStateSpaceModel ▪ ModelPredictiveController ▪ NicholsGridLines ▪ NicholsPlot ▪ NonlinearStateSpaceModel ▪ NyquistGridLines ▪ NyquistPlot ▪ ObservabilityGramian ▪ ObservabilityMatrix ▪ ObservableDecomposition ▪ ObservableModelQ ▪ OutputControllabilityMatrix ▪ OutputControllableModelQ ▪ OutputResponse ▪ PhaseMargins ▪ PhaseRange ▪ PIDData ▪ PIDDerivativeFilter ▪ PIDFeedforward ▪ PIDTune ▪ PoleZeroMarkers ▪ RootLocusPlot ▪ SamplingPeriod ▪ SingularValuePlot ▪ SmithDelayCompensator ▪ StabilityMargins ▪ StabilityMarginsStyle ▪ StateFeedbackGains ▪ StateOutputEstimator ▪ StateResponse ▪ StateSpaceModel ▪ StateSpaceRealization ▪ StateSpaceTransform ▪ StateTransformationLinearize ▪ SystemsConnectionsModel ▪ SystemsModelControllerData ▪ SystemsModelDelay ▪ SystemsModelDelayApproximate ▪ SystemsModelDelete ▪ SystemsModelDimensions ▪ SystemsModelExtract ▪ SystemsModelFeedbackConnect ▪ SystemsModelLabels ▪ SystemsModelLinearity ▪ SystemsModelMerge ▪ SystemsModelOrder ▪ SystemsModelParallelConnect ▪ SystemsModelSeriesConnect ▪ SystemsModelStateFeedbackConnect ▪ SystemsModelVectorRelativeOrders ▪ ToContinuousTimeModel ▪ ToDiscreteTimeModel ▪ TransferFunctionCancel ▪ TransferFunctionExpand ▪ TransferFunctionFactor ▪ TransferFunctionModel ▪ TransferFunctionPoles ▪ TransferFunctionZeros ▪ InputOutputResponse ▪ InputOutputResponseData ▪ RiccatiSolve ▪ DiscreteRiccatiSolve ▪ LyapunovSolve ▪ DiscreteLyapunovSolve ▪ SystemModelExamples ▪ SystemModel ▪ SystemModels ▪ SystemModelSimulate ▪ SystemModelMeasurements ▪ SystemModelSimulationData ▪ SystemModelSimulateSensitivity ▪ SystemModelPlot ▪ ParametricPlot ▪ Plot ▪ ListLinePlot ▪ LogPlot ▪ SystemModelParametricSimulate ▪ ParametricFunction ▪ NMinimize ▪ FindMinimum ▪ NMaximize ▪ SystemModelLinearize ▪ FindSystemModelEquilibrium ▪ ConnectSystemModelController ▪ SystemModelReliability ▪ ReliabilityDistribution ▪ SurvivalFunction ▪ StructuralImportance ▪