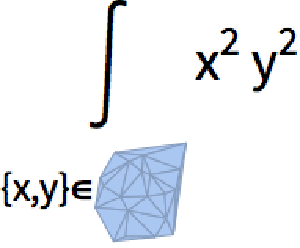Data and Mesh Regions
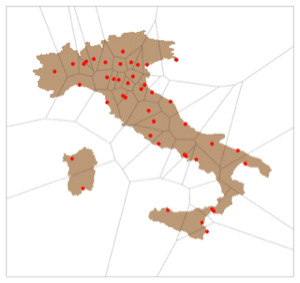
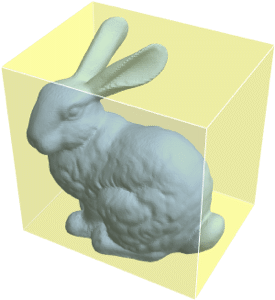
Version 10 adds full support for mesh-based geometric regions. Mesh-based regions can be explicitly specified or automatically generated from lists of points, from graphics, or from other regions. Mesh-based regions are flexible enough to approximate any other region and support fast algorithms for essentially any operation. The mesh-based regions fully support the geometric region framework, including computing properties (area, nearest point, etc.) and being used as inputs to solvers (integration, solving PDEs, etc.).
- Full support for meshes in 1D, 2D, and 3D. »
- Ability to represent low-dimensional regions, e.g. curves in 2D, surfaces in 3D.
- Ability to represent non-manifold regions.
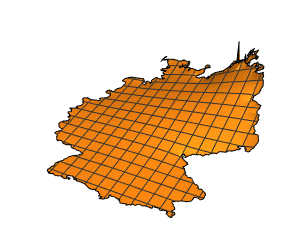
- Full support for boundary representation meshes in 1D, 2D, and 3D. »
- Ability to represent holes in 2D, as well as voids and tunnels in 3D.
- High-level support for styling and labeling of mesh cells. »
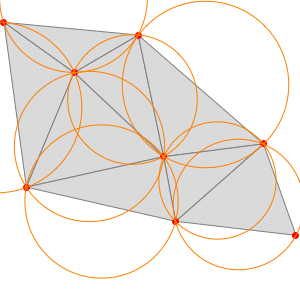
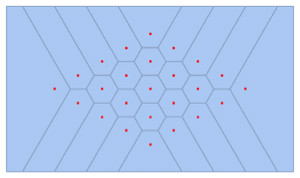
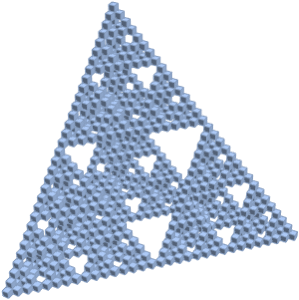
- Mesh generation from point sets, including Delaunay, Voronoi, and convex hull.
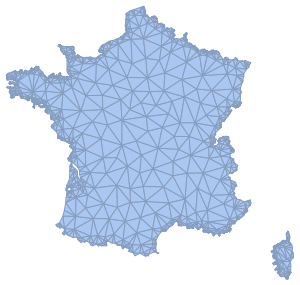
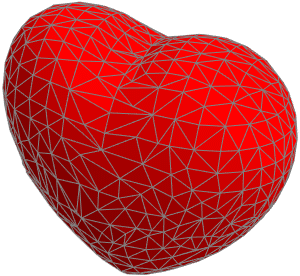
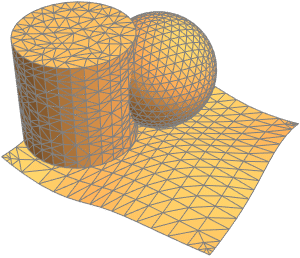
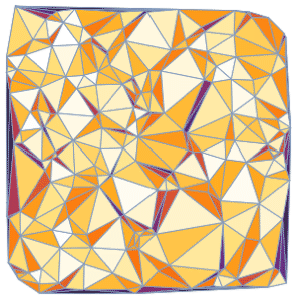
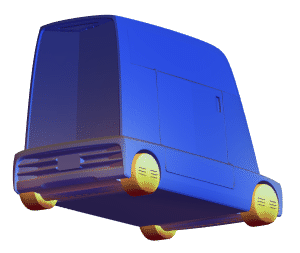
- Support for mesh triangulation with high-level controls. »
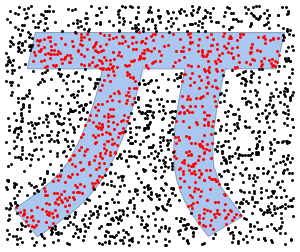
- Automatic discretization of 2D and 3D graphics. »
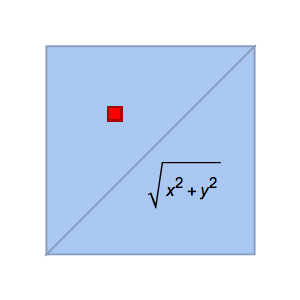
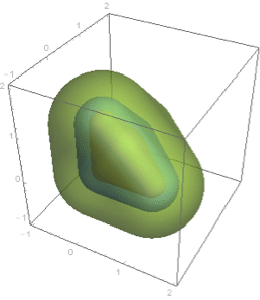
- Automatic discretization of any region. »
- Full support for computing key region properties such as membership test, distance computation, nearest points, measure (length, area, volume), centroids, etc. »
- Integrate over mesh-based regions. »
- Solve partial differential equations over mesh-based regions. »
- Support for low-level programming operations involving cells and coordinates.
- Support for cell-level properties, for instance, to store material or other properties.