Data Science and Report Generation
The Wolfram Language has what you need to process data and publish professional reports.
Data Acquisition
Importing Data from Files
In order to do data science, you need data, and the Wolfram Language comes with many ways to easily access the data you need. The built-in Import function will import several hundred kinds of commonly used file formats.
1. Import data using the default settings.
Import will automatically import most common file formats as a suitable expression:

If Import cannot determine the format of a file, you can specify it explicity:
It's also easy to import data into a Dataset object, a structured dataset based on a hierarchy of lists and associations. This makes it easy (and fast) to traverse large datasets.
2. Import data as a Dataset.
Data-oriented formats such as CSV, TSV, XLS and XLSX will import as a Dataset. Specify "Dataset" as the second argument to Import.
Import will automatically import most common file formats as a suitable expression:

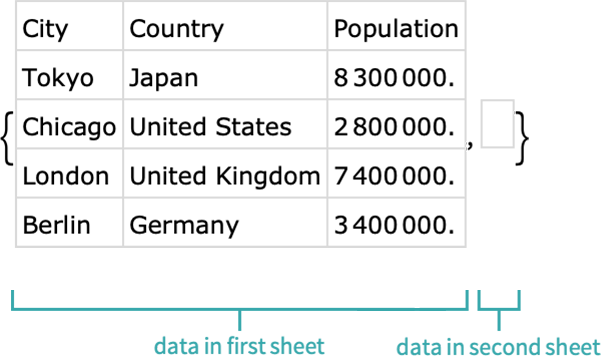
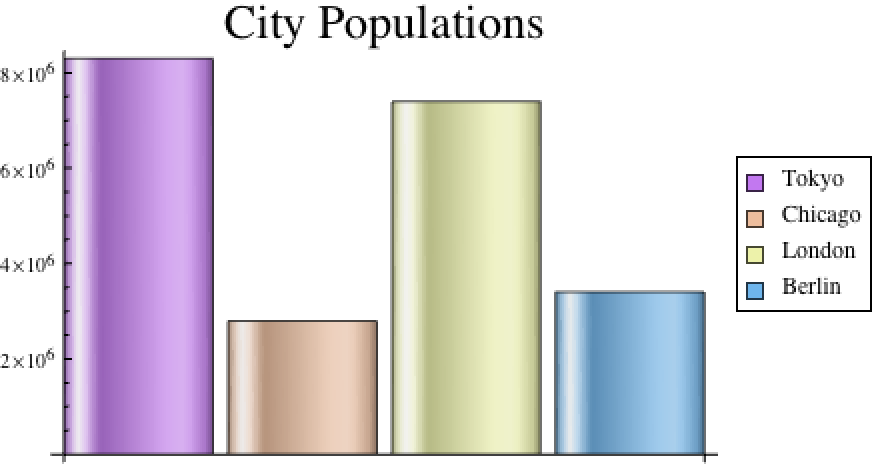
Often, you'll want to extract a particular element from a dataset without having to import the whole dataset and then extract it. Using an additional parameter, the Import function can extract particular elements.
3. Import particular elements from a data file or webpage.
Many files and webpages contain elements other than the data returned by default by Import. Get a list of elements by giving "Elements" as the second argument to Import.
Import will automatically import most common file formats as a suitable expression:

Specify which element to import:
Importing Data from an API
The Wolfram Language makes it easy to connect to external services. In this example, data is accessed via an API about the location of bikeshares in London:
Analysis and Visualization
Automated Analysis
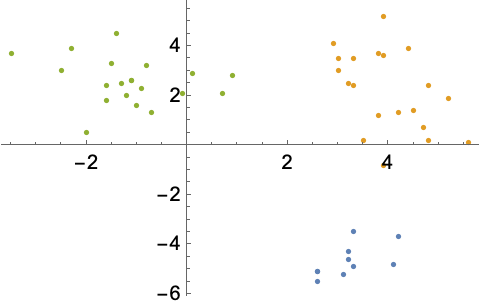
The Wolfram Language has thousands of built-in functions that allow you to focus on your project, not the technicalities of how specific actions are formed. While you can fully specify every detail, the default settings for the functions are designed to work the best in almost all cases, resulting in short, readable code, even for very complex tasks. In this example, bivariate data is automatically clustered with the FindClusters function.
Find and visualize clusters in bivariate data:

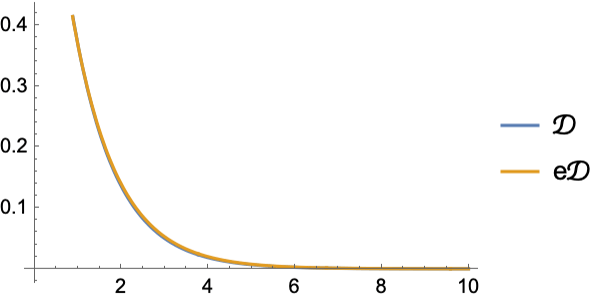
High-level functions like FindDistribution can analyze your data and figure out which of over 35 distributions best fits your data using a variety of statistical methods.
Generate data sampled from an exponential distribution:
Find the best distribution from the data:
Compare the PDFs for the original and estimated distributions:
Cloud Deployment
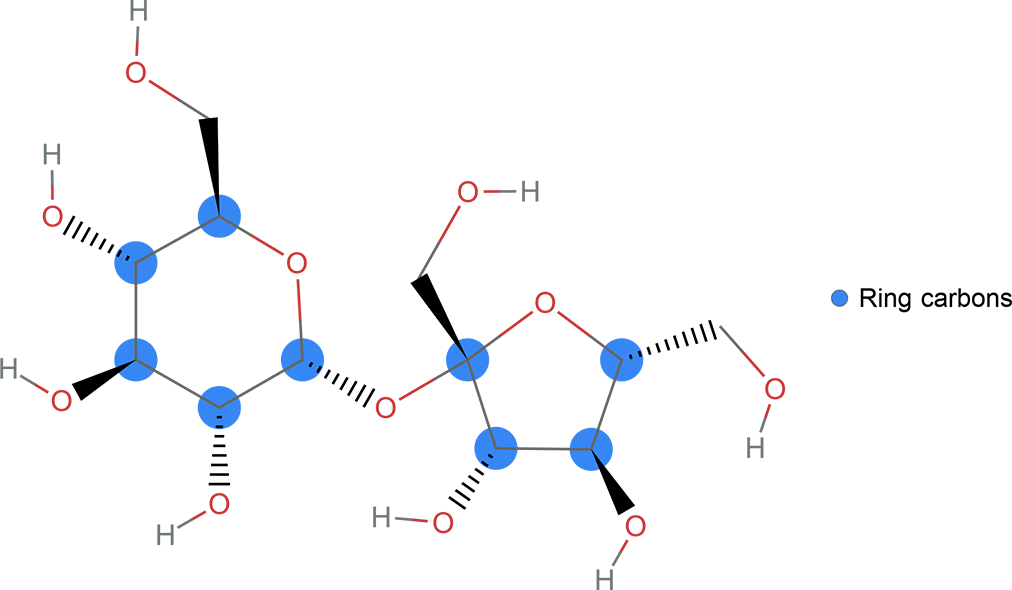
You will often want to share a program with others, and the Wolfram Language makes it easy to turn your code into a standalone, interactive webpage. Using the CloudDeploy function, your code will be published to Wolfram Research servers and be made accessible to either everyone or to whomever you grant permission. In this example, an interactive program for recognizing an image of a molecule is turned into a public webpage.
1. Make the content to be published:
Get Started
Learning Resources
Learning Paths
 Try it now, learn later
Try it now, learn later
Want to just try it out? Get a feel for what the Wolfram Language is like while trying out real code samples focused on building and deploying web applications.
 Get certified for free in the Wolfram Language
Get certified for free in the Wolfram Language
We've made it easy to learn the Wolfram Language your way. Try our free interactive course and earn a certification.
Go Further with Data Science
If you want to see more of what Wolfram offers for data science, read about the Wolfram approach to data science & AI. You'll find:
- Downloadable examples
- Links to documentation
- Talks, presentations and lectures
- Online classes
- Techical information
Recommended Product
For Those Interested in Data Science, We Recommend:

Our cloud-desktop hybrid product, Wolfram|One, is our recommended environment for those interested in data science: it has an award-winning intuitive notebook interface, seamless functionality with the cloud and is the complete Wolfram experience.
Explore Other Topics
Data Science and Report Generation

Explore tools for analysis, automatically import data, deploy cloud dashboards and more.
Machine Learning

Explore neural networks, automated machine learning, classifiers and more.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies

Explore blockchains, chart cryptocurrencies, use cryptographic functions and more.
Build and Deploy Web Applications

Explore easily deployed web applications, turn your code into real websites and more.
Financial Technology

Explore financial data, make charts, write prediction functions and more.
Geography and GIS

Explore various map-making methods, superimpose data, create visualizations and more.

