| More about Mathematica » |
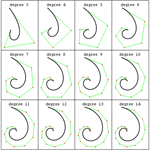
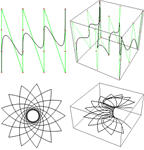
Mathematica 7 introduces highly general systemwide support for splines—covering Bézier curves, B-spline curves and surfaces and NURBS curves and surfaces, all with any degree, and in any number of dimensions. In addition to complete integration with 2D and 3D graphics, as well as with interpolation, Mathematica 7 for the first time provides full exact symbolic handling of splines, making it possible to take advantage of spline methods in many new mathematical settings.
- Industrial-strength B-spline and NURBS-based curve and surface graphics primitives. »
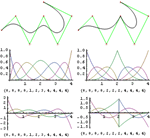
- Arbitrary-degree, composite Bézier and B-spline curves and surfaces. »
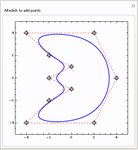
- Settable control points, degrees, knots, periodicity and weights in B-splines and NURBS. »
- Support for automatic degree selection and knot generation in B-splines and NURBS.
- Integrated spline-based 3D tubes with detailed coloring and radius control. »
- Dynamic and interactive manipulation of the spline-based curves.
- Support for time-varying splines for keyframing, etc.
- Direct import and export of Bézier curves in PostScript, PDF and SVG formats. »
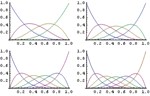
- Symbolic and numerical Bernstein polynomial and B-spline basis functions. »
- Support for spline functions in any number of dimensions.
- Support for spline-based manifolds with any codimension and any embedding dimension.
- Symbolic manipulation of spline functions, including integration, differentiation and piecewise expansion.
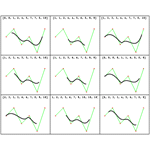
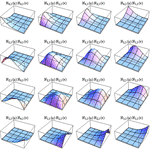
- Support for spline-based interpolation, with arbitrary continuity order. »
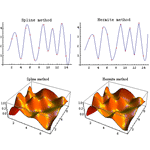
- Built-in spline interpolation option in data visualization functions.