乾燥摩擦のある車輪
車輪付きの車は5000年以上に渡って重要な運送手段となっていますが,車輪表面の動的挙動はいまだに理解が難しいものです.ここでは軸を中心として一定のトルクで駆動されたときに,乾燥摩擦付きでモデル化された車輪がどのように振る舞うかを調べます.
モデル
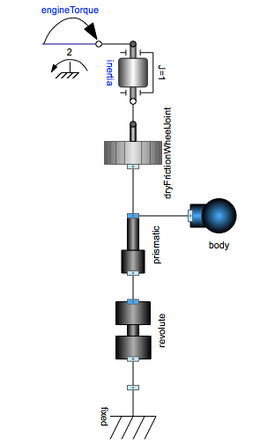
車輪についてのバーチャルのテスト装置.すべてのモデルコンポーネントはPlanarMechanicsライブラリと組込みライブラリで利用可能である.
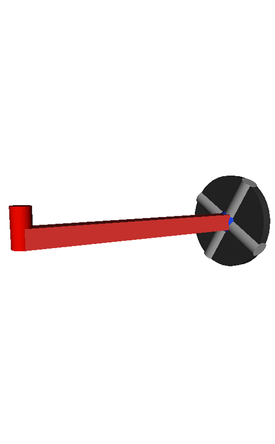
生成されたテスト装置の3Dビュー
シミュレーション結果
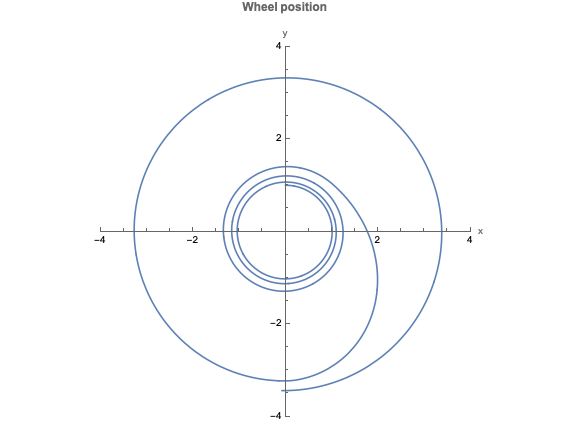
車輪が加速し始めると,横滑りのために中心からの距離が大きくなる.最初横滑りは小さく,車輪はほぼ理想的な円を描いて動く.しかし遠心力のために滑り速度が大きくなると,車輪は滑り始める.
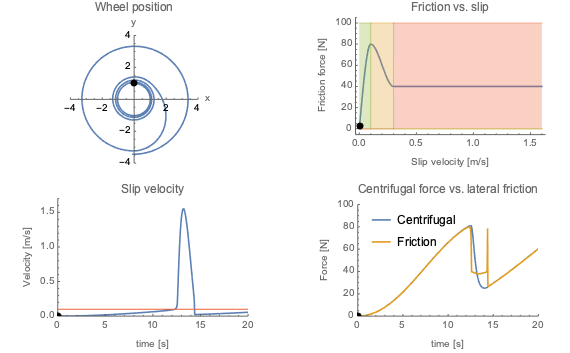
車輪の滑りは,車輪上の摩擦力を滑り速度の関数として調べることで理解できる.滑り速度がある点に達すると,摩擦力は減少し滑りが始まり,車輪の中心までの距離は急速に増大する.距離が十分な長さになると遠心力は摩擦力より小さくなり滑り速度が低下し車輪は再び円状に動く.
Wolfram System Modeler
評価版
ご購入
System ModelerはWindows,macOS,
Linuxで日本語と英語でご利用になれます »
ご質問やコメントはWolframエキスパートまでお寄せください »