Ranges of Values of the Earth's Magnetic Field
The new functions CoordinateBounds and CoordinateBoundingBox allow you to find the extrema values in each dimension of a multidimensional array. This example finds the ranges of values of the Earth's magnetic field in a given region.
Define a region near the North Pole from its latitudes and longitudes.
In[1]:=
lat = {65, 85};
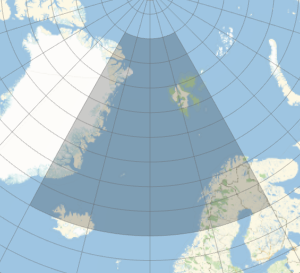
lon = {-30, 30};Plot this region on a world map.
In[2]:=
GeoGraphics[GeoBoundsRegion[{lat, lon}], GeoGridLines -> Automatic,
GeoZoomLevel -> 5]Out[2]=
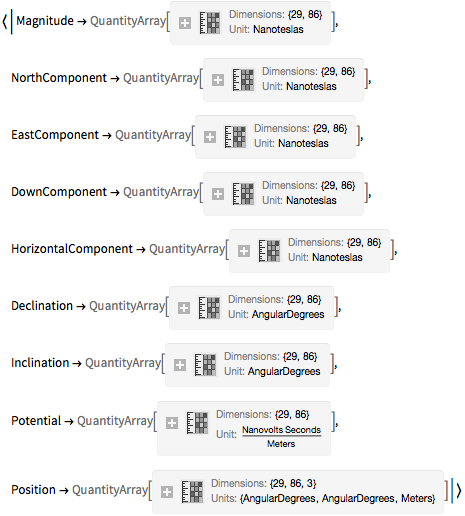
Generate the data of the Earth's magnetic field in this region.
In[3]:=
data = GeomagneticModelData[Transpose[{lat, lon}], GeoZoomLevel -> 1]Out[3]=
Extract from this data the components of the Earth's magnetic field.
In[4]:=
components = {"NorthComponent", "EastComponent", "DownComponent"};
arr = Lookup[data, components]Out[4]=
Convert the list of arrays into an array of 3-vectors.
In[5]:=
qa = Transpose[QuantityArray[arr], {3, 1, 2}]Out[5]=
These are the ranges of the components of the Earth's magnetic field in the specified region.
In[6]:=
Thread[components -> CoordinateBounds[qa]]Out[6]=